The Pocket Guide to the Operating Room by Maxine Goldman is a concise resource for surgical teams, providing essential protocols and best practices for efficient OR management․
Overview of the Guide
The Pocket Guide to the Operating Room by Maxine Goldman offers a comprehensive yet concise overview of OR operations, covering essential protocols, safety measures, and efficiency tips․ It serves as a quick reference for surgical teams, detailing roles, equipment, and procedures․ The guide emphasizes practical applications, ensuring clarity and accessibility for both experienced professionals and newcomers․ Its structured approach makes it an invaluable resource for maintaining high standards in surgical care․
Importance of the Operating Room in Healthcare
The operating room (OR) is a critical space in healthcare, serving as the hub for surgical interventions, emergency procedures, and specialized treatments․ It plays a vital role in improving patient outcomes, enabling life-saving surgeries, and addressing complex medical conditions․ A well-functioning OR ensures timely and effective care, adapting to advancements in technology and medical practices․ Its importance extends to training future healthcare professionals, making it a cornerstone of modern healthcare delivery․
Target Audience for the Guide
The Pocket Guide to the Operating Room is designed for surgical professionals, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and surgical technologists․ It serves as a practical resource for residents, medical students, and experienced practitioners seeking to refine their skills․ Hospital administrators and OR managers also benefit from its insights on efficient workflow and safety protocols․ The guide is tailored to ensure all OR personnel can access standardized protocols and evidence-based practices, fostering excellence in patient care․
History and Evolution of the Operating Room
The operating room has evolved from primitive surgical spaces to modern, high-tech environments․ Maxine Goldman’s guide reflects this progression, emphasizing safety, efficiency, and standardized practices․
Early Developments in Surgical Spaces
The earliest surgical spaces were rudimentary, often lacking proper sanitation and lighting․ Over time, the introduction of anesthesia and antiseptic practices transformed these areas into more controlled environments․ Maxine Goldman’s guide highlights how these early advancements laid the foundation for modern surgical standards․
Early operating rooms evolved from basic setups to spaces with specialized tools and protocols․ This historical progression is crucial for understanding the development of efficient and safe surgical practices, as outlined in Goldman’s comprehensive guide․
Key Milestones in Operating Room Technology
Advancements in operating room technology have significantly improved surgical outcomes․ Key milestones include the development of anesthesia machines, surgical lighting, and sterilization equipment․ Modern innovations like robotic-assisted surgery and real-time monitoring systems have further enhanced precision and safety․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes these technological evolutions, highlighting their role in creating efficient and patient-centered surgical environments․ These advancements continue to shape the future of operating room practices․
The Role of Maxine Goldman in Modern Operating Room Practices
Maxine Goldman has significantly influenced modern operating room practices through her comprehensive guides and emphasis on standardized protocols․ Her work focuses on improving efficiency, safety, and communication among surgical teams․ Goldman’s contributions have streamlined workflows, reducing errors and enhancing patient care․ Her insights are widely recognized, making her a pivotal figure in contemporary OR education and practice․
By advocating for evidence-based practices, Goldman ensures that surgical teams adhere to the highest standards․ Her dedication to continuous improvement has made her a trusted resource in the field, fostering better outcomes for patients and professionals alike․

Key Roles in the Operating Room
The operating room relies on surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and technologists working cohesively to ensure patient safety and procedural success․ Each role is vital, contributing uniquely to efficient and effective surgical outcomes․
The Surgeon’s Responsibilities
The surgeon is the primary leader in the operating room, responsible for performing surgical procedures with precision and care․ They assess patients preoperatively, develop surgical plans, and ensure patient safety․ During surgery, surgeons maintain focus to execute procedures accurately, collaborating with anesthesiologists and nurses․ Post-operatively, they oversee recovery and manage complications․ Their expertise and decision-making are critical to successful outcomes․ Maxine Goldman emphasizes the surgeon’s role in fostering a coordinated and efficient OR environment․
The Role of Anesthesiologists
Anesthesiologists play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and comfort during surgery․ They evaluate patients preoperatively, administer anesthesia tailored to individual needs, and monitor vital signs intraoperatively․ Their expertise in pain management and life support is vital․ Maxine Goldman highlights their collaboration with surgeons and nurses to maintain a safe and efficient OR environment․ Anesthesiologists balance technical skills with compassionate care, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients undergoing surgical procedures․
Nursing Staff in the Operating Room
Nursing staff are essential to the smooth operation of the OR, ensuring patient safety and care throughout surgical procedures․ They prepare operating rooms, sterilize equipment, and assist surgeons and anesthesiologists․ Maxine Goldman emphasizes their role in maintaining a sterile environment and monitoring patient vital signs․ Nurses also provide pre- and post-operative care, educating patients on recovery processes․ Their attention to detail and teamwork are critical for efficient and safe surgical outcomes, making them indispensable in the OR setting․
The Importance of Surgical Technologists
Surgical technologists play a vital role in the operating room, ensuring the smooth progression of surgical procedures․ They prepare the OR by sterilizing equipment and arranging instruments, assist surgeons during operations, and maintain a sterile environment․ Maxine Goldman highlights their expertise in handling surgical instruments and their adaptability during complex procedures․ Their attention to detail and ability to anticipate surgeons’ needs make them indispensable in ensuring patient safety and operational efficiency in the surgical setting․
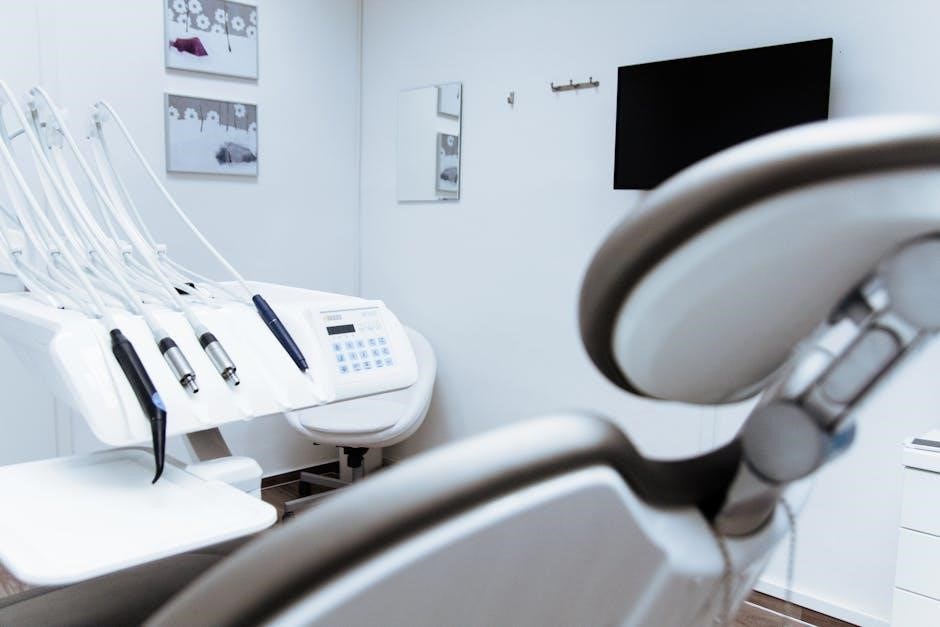
Setting Up the Operating Room
Setting up the OR involves meticulous planning, from layout design to arranging essential equipment․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes proper sterilization and organization to ensure efficiency and safety in surgical procedures․
Design and Layout of the Operating Room
The design and layout of the operating room are crucial for efficiency and patient safety․ Maxine Goldman’s guide highlights the importance of a well-organized space, ensuring easy access to equipment like anesthesia stations, surgical lighting, and instrument tables․ A modular layout allows for flexibility, accommodating various procedures while maintaining sterility․ Ergonomic design reduces staff fatigue and enhances teamwork, creating an optimal environment for surgical success․
Essential Equipment for Modern Surgery
Modern operating rooms rely on advanced equipment to ensure safe and effective surgeries․ Ventilators, anesthesia machines, and surgical lights are critical for patient monitoring and visibility․ Electrosurgical units, laparoscopic tools, and robotic systems enhance precision․ Monitoring devices track vital signs, while sterile supply systems maintain hygiene․ Endoscopy equipment and imaging technologies aid minimally invasive procedures․ According to Maxine Goldman, having the right tools ensures efficiency, safety, and optimal patient outcomes in today’s surgical environments․
Sterilization and Preparation Processes
Sterilization is critical for preventing infections and ensuring patient safety․ Autoclaving, chemical disinfection, and ultraviolet light are common methods․ Instruments are packaged and stored to maintain sterility․ The surgical team follows strict preparation protocols, including gowning and gloving․ Maxine Goldman emphasizes proper organization and labeling of equipment․ Efficient preparation ensures smooth operations and reduces contamination risks, adhering to high surgical standards and promoting a safe environment for both patients and staff․
Surgical Instruments and Tools
Surgical instruments are essential for precision and safety․ Basic tools include scalpels, forceps, and retractors․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes proper organization and handling to ensure efficiency and sterility;
Common Surgical Instruments
Common surgical instruments include scalpels, forceps, retractors, and suction tubes․ These tools are essential for precise tissue handling and maintaining a clear surgical field․ According to Maxine Goldman’s guide, proper identification and organization of instruments are critical for efficiency․ Each tool is designed for specific tasks, such as cutting, clamping, or exposing tissue․ Their effective use ensures optimal surgical outcomes and patient safety, making them indispensable in every operating room setting․
Advanced Tools in Modern Surgery
Advanced tools in modern surgery include robotic systems, laparoscopic instruments, and laser technology․ These innovations enhance precision, minimize invasiveness, and improve patient outcomes․ According to Maxine Goldman’s guide, such tools are transforming surgical practices, enabling complex procedures with reduced recovery times․ Their integration into operating rooms highlights the evolution of surgical techniques, emphasizing the importance of staying updated with cutting-edge technology for optimal care and efficiency in the OR environment․
Proper Handling and Maintenance of Instruments
Proper handling and maintenance of surgical instruments are critical for ensuring sterility, functionality, and longevity․ According to Maxine Goldman’s guide, instruments should be cleaned immediately after use, avoiding harsh chemicals that may cause damage․ Sterilization methods like autoclaving are essential before and after procedures․ Regular inspections and proper storage in designated areas help prevent wear and tear․ Adhering to manufacturer guidelines ensures optimal performance and patient safety, making maintenance a priority in the operating room environment․

Surgical Procedures and Protocols
Surgical procedures and protocols ensure standardized practices, prioritizing patient safety and efficiency․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes adherence to established guidelines, minimizing risks, and optimizing outcomes in the OR․
Pre-Operative Preparation
Pre-operative preparation is a critical phase ensuring patient readiness for surgery․ It involves thorough medical assessments, obtaining informed consent, reviewing lab results, and planning anesthesia․ Patients are educated on fasting rules, medication adjustments, and post-surgery expectations․ Verification of surgical site and medical history is essential․ Proper preparation minimizes risks, ensures safety, and streamlines the surgical process, aligning with Maxine Goldman’s guidelines for efficient and safe OR practices․
Intraoperative Care and Monitoring
Intraoperative care focuses on maintaining patient stability during surgery․ Continuous monitoring of vital signs, anesthesia management, and surgical site preparation are crucial․ The surgical team ensures asepsis, handles instruments efficiently, and communicates clearly․ Anesthesiologists monitor anesthesia depth, while nurses manage patient positioning and fluid balance․ Maxine Goldman’s guidelines emphasize precise documentation and real-time adjustments to ensure optimal outcomes and patient safety throughout the procedure․
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Post-operative care ensures patient recovery and comfort after surgery․ Monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and preventing complications are priorities․ Patients are observed in recovery rooms, where anesthesia effects are closely watched․ Wound care, fluid balance, and medication administration are critical․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes clear communication between surgical teams and post-op staff to optimize recovery outcomes and minimize risks, ensuring a smooth transition to patient discharge or further care․
Patient Safety in the Operating Room
Patient safety is paramount, involving strict protocols, teamwork, and continuous monitoring to minimize risks and ensure optimal outcomes during surgical procedures․
Ensuring Patient Safety
Patient safety is achieved through rigorous protocols, verification processes, and meticulous surgical site marking․ Proper anesthesia administration, instrument management, and clear communication are essential․ Goldman’s guide emphasizes teamwork and adherence to evidence-based practices to minimize risks and ensure optimal outcomes․ Regular training and compliance with safety standards further enhance the OR environment, prioritizing patient well-being above all․
Common Risks and Complications
Common risks in the OR include surgical site infections, bleeding, and anesthesia-related complications․ Airway obstruction, cardiac events, and allergic reactions are also potential concerns․ Goldman’s guide outlines these risks and provides strategies to mitigate them, emphasizing the importance of verification processes and clear communication among surgical teams to ensure patient safety and minimize adverse outcomes during and after surgery․
Strategies for Error Prevention
Strategies for error prevention in the OR include rigorous pre-operative checklists, clear communication protocols, and verification processes․ Goldman’s guide emphasizes the importance of surgical time-outs to ensure patient identification and procedure verification․ Proper training, adherence to safety protocols, and continuous monitoring of equipment and patient vital signs are also critical․ These strategies aim to minimize human error, enhance teamwork, and improve patient outcomes, aligning with Goldman’s focus on standardized, evidence-based practices․

Anesthesia and Pain Management
Anesthesia and pain management are critical components of surgical care, ensuring patient comfort and safety․ Goldman’s guide provides insights into anesthesia administration, monitoring techniques, and post-operative pain relief strategies․
Types of Anesthesia
Types of anesthesia include local, regional, and general anesthesia․ Local numbs a specific area, regional affects a larger section, and general induces unconsciousness․ Conscious sedation provides relaxation without full unconsciousness․ Each type is tailored to the procedure and patient needs, ensuring optimal pain management and patient safety during surgery․
Pain Management Techniques
Pain management techniques in the operating room involve a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods․ These include the use of opioids, NSAIDs, and regional anesthesia to block pain signals․ Non-pharmacological approaches, such as nerve blocks and acupuncture, are also employed․ Effective pain management enhances patient comfort, reduces stress, and supports faster recovery․ Tailoring techniques to individual needs ensures optimal outcomes and minimizes post-operative discomfort․
Risks and Side Effects of Anesthesia
Anesthesia carries potential risks and side effects, including nausea, dizziness, and respiratory complications․ Short-term effects may involve confusion or sore throat, while rare cases can lead to organ damage or allergic reactions․ Individual health conditions, such as heart disease, increase vulnerability․ Proper monitoring and personalized anesthesia plans help minimize these risks, ensuring patient safety and optimal recovery outcomes․

Emergency Procedures in the Operating Room
Emergency procedures in the OR require swift action and clear communication․ Protocols for fire, cardiac arrest, and system failures ensure patient and staff safety, minimizing complications․
Handling Surgical Emergencies
Handling surgical emergencies requires immediate action and a well-coordinated team․ Protocols like rapid response systems and emergency checklists ensure prompt intervention․ Effective communication and clear roles minimize delays․ Prioritizing patient safety, surgical teams must remain calm and decisive․ Essential equipment and backup supplies should always be readily available․ Continuous training and drills prepare staff for unexpected scenarios, ensuring optimal outcomes during critical situations․
Fire Safety in the Operating Room
Fire safety in the OR is critical due to the presence of flammable materials and electrical equipment․ Preventive measures include proper storage of flammable substances and regular checks of electrical devices․ Staff must be trained in fire response, with fire extinguishers and emergency exits easily accessible․ Protocols for fire emergencies should be clearly outlined and practiced, ensuring patient and team safety during any incident․ Vigilance and preparedness are essential to mitigate fire risks in the surgical environment․
Cardiac Arrest and Other Critical Situations
In the operating room, cardiac arrest and other critical situations demand immediate action․ The surgical team must be prepared to respond swiftly, following established protocols․ Defibrillators, medications, and emergency airway tools should be readily available․ Communication and coordination among surgeons, anesthesiologists, and nurses are crucial to ensure patient survival․ Regular training and drills help maintain readiness for such high-stakes scenarios, emphasizing the importance of teamwork and adherence to life-saving procedures․
Infection Control and Sterilization
Infection control and sterilization are critical in surgical settings to ensure patient safety․ The guide outlines best practices, including proper cleaning, disinfection, use of PPE, and handling of instruments to minimize contamination risks․
Importance of Infection Control
Infection control is vital to prevent hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) and ensure patient safety․ Proper sterilization and hygiene practices reduce the risk of surgical site infections, protecting both patients and staff․ Adherence to infection control protocols minimizes complications, promotes recovery, and maintains trust in healthcare services․ Effective infection control is a cornerstone of modern surgical practices, as emphasized in Maxine Goldman’s guide․
Sterilization Methods
Sterilization methods are critical for eliminating pathogens in the OR․ Autoclaving uses high-pressure steam, while dry heat sterilization employs hot air․ Chemical methods, like ethylene oxide, are used for heat-sensitive items․ Filtration is applied to liquids and gases․ These techniques ensure all equipment is safe for use, preventing infections and maintaining patient safety, as outlined in Maxine Goldman’s guide․
Preventing Hospital-Acquired Infections
Preventing hospital-acquired infections requires strict adherence to evidence-based protocols․ Proper hand hygiene, use of PPE, and sterile technique are essential․ Regular environmental cleaning and sterilization of instruments reduce pathogen transmission․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes staff education and monitoring to ensure compliance with infection control practices, minimizing risks for patients and maintaining a safe surgical environment․
- Adhere to hand hygiene protocols․
- Use PPE correctly․
- Maintain sterile technique․
- Ensure proper environmental cleaning․
- Sterilize instruments thoroughly․
- Monitor and educate staff․
The Pocket Guide to the Operating Room by Maxine Goldman provides invaluable insights, fostering continuous improvement in surgical practices․ Future advancements in technology and education will further enhance OR efficiency and patient outcomes․
The Pocket Guide to the Operating Room by Maxine Goldman emphasizes infection control, patient safety, and surgical team collaboration․ It highlights efficient OR setup, essential instruments, and adherence to protocols․ Goldman underscores the importance of continuous learning and evidence-based practices, ensuring optimal outcomes․ This guide serves as a foundational resource for surgical professionals, bridging theory and practical application in modern operating rooms․
Future Trends in Operating Room Practices
Future trends in operating room practices include advancements in AI-driven surgical tools, robotic-assisted surgeries, and enhanced telemedicine integration․ Maxine Goldman’s guide highlights the potential for real-time data analytics to improve patient monitoring․ Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability in OR operations and the use of virtual reality for surgical training․ These innovations aim to enhance efficiency, reduce complications, and improve patient outcomes in modern healthcare settings․
Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Continuous learning is crucial for operating room professionals to stay updated on best practices and technological advancements․ Maxine Goldman’s guide emphasizes the importance of ongoing education through certifications, workshops, and online courses․ Staying informed about industry advancements ensures improved patient care and operational efficiency․ Encouraging a culture of lifelong learning fosters collaboration and adaptability among surgical teams, ultimately enhancing overall healthcare outcomes and professional growth․

References and Further Reading
Key resources include textbooks like Pocket Guide to the Operating Room and online tools for surgical professionals, providing comprehensive insights and updated practices in OR management․
Recommended Textbooks and Guides
Key resources include Pocket Guide to the Operating Room by Maxine Goldman, offering concise surgical protocols․ Other essential guides like Surgical Technology for the Surgical Technologist and Alexander’s Care of the Patient in Surgery provide comprehensive insights․ Online platforms and educational DVDs further enhance learning, ensuring practical and evidence-based approaches for OR professionals․
Online Resources for Surgical Professionals
Key online resources include the Association of Surgical Technologists (AST) and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) websites, offering evidence-based guidelines․ Platforms like Google Scholar and PubMed provide access to medical journals․ Additionally, advanced search techniques and tools like Google Lens enable quick access to surgical information, while Google’s unit conversion and calculator features support precise intraoperative calculations, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in surgical environments․
Journals and Publications
Key journals such as Journal of Surgical Research and AORN Journal provide essential evidence-based insights for surgical professionals․ These publications, alongside Maxine Goldman’s guide, offer comprehensive coverage of surgical practices․ The guide complements these journals with concise, practical information on infection control, surgical protocols, and OR management, serving as an indispensable resource for maintaining high standards and staying updated in the field․